A project of the Robotics 2020 class of the School of Information Science and Technology (SIST) of ShanghaiTech University. Course Instructor: Prof. Sören Schwertfeger.
Yuanyuan Yang,Lei Jia
1 Introduction
This project presents a simple distributed upper computer system which can be used for mapping robot to solve the data collection problem which can be found with a huge amount of sensors input. In the project we use 12 mini PC with other different sensors to build a simple test distributed system. The system’s structure is similar to a multi-robots system with HPRC (High Performance Robotic Computing), so it may also use the same technique on HPC (High Performance Computing) to improve the computing ability of the system.
Nowadays when building an advanced mapping platform, the requirement of collection high quality data especially in collection robot data-sets makes a great challenge on the I/O ability of the robot’s computer system. The simple idea is to use a distributed system to disperse the data from different sensor. Therefore, we attempt to build a simple distributed system which can achieve the collection of high frequency and high quality data from multi-sensors robots. This system should be stable and easy to use. There is possibility to improve the system with technique in HPC and multi-robot system.
2 System Description
Taking into account that the mapping platform we build needs to collect high-quality data, we can adopt the strategy of connecting multiple computers to different sensors to build a distributed system in order to achieve the desired effect. In the early stage, we have tested, a NUC8 connected to a PointGrey camera, the frequency can reach 60Hz, and a more powerful computer connected, the frequency can not reach the desired level. Therefore, we finally decided to adopt a distributed system to build a mapping platform.
2.1 System Structure

The nodes in this system are mini PCs. This system has 12 such mini PCs’s connected with ROS via a local area network (LAN). One of the master node control all the other nodes which are connected with sensors. Considering we don’t have the 12 mini PCs now, we use a desktop computer as the master node, a NUC8 and a big laptop as slave nodes, and the switches form a local area network. The hardware structure of the distributed system of this project is shown below.
2.2 Main Function
In order to make the system easy to use, some functions that facilitate the operation of the distributed system need to be implemented.
2.1.1 Wake on LAN
To realize poweron and shutdown computer from master PC through the network. The following things need to be done:
1) Poweron slave PCs
Firstly, install wakeonlan and check whether the network card support wakeonlan or not. In addtion, change the Power On by Onborad Lan of bois to enable, and record IP and MAC address of every slave PC. Master PC can poweron slave PCs by $wakeonlan [MACaddress].
2) Shutdown slave PCs
SSH password-free login is required. Then write a script to shutdown all of slave PCs.
2.1.2 Manage apps
To realize the system stable and easy to use, a visual management tool to start and close the slave nodes apps is needed. MARS Lab have an existing management tool called app_manager which can be reused.
It has two parts: client and manager. Client realizes an GUI which makes it easy to control and manange the apps of slaves. Manager realizes start apps of slaves from master through LAN. It was originally developed for communication between two computers. But for more than 2 PCs, we need to improve it.
1) Naming conflict
Due to the need to modify multiple names, a script that can quickly modify names is written using sed and regular expressions.
2) Client program
We read the source code and made some logical changes.
Considering before starting apps from client had been installed on the master, slaves should launch manager firstly. We need to make the manager start automatically on boot on slaves. There are many ways to achieve this. We finally adopted the method of adding a script of starting app_manager in the Linux GNOME desktop system. In the “Startup Application Preferences”, we can set the automatic startup program at boot.
2.1.3 Monitoring
In order to ensure the system runs stablly. A good way to monitor 12 computers is needed. It can see if they are running, and if the system is healthy, maybe even to see CPU status, memory usage of each computer.
Now, we use a management tool called Ganglia to monitor mini PCs. Ganglia is an open source cluster monitoring tool designed to measure thousands of nodes. It is mainly used to monitor system performance, such as: cpu, memory, hard disk utilization, I/O load, network traffic, etc. It is easy to see the working status of each node through the curve. And it plays an important role in adjusting and allocating system resources properly of the overall system performance. The workflow of ganglin is shown below.
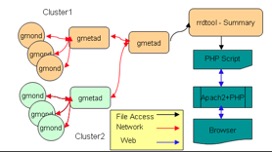
2.1.4 NTP synchronization between computers
Use NTP protocol. NTP is a network time synchronization protocol that can synchronize the time of various computers on the network. Time synchronization can be achieved by installing the NTP package and modifying the corresponding server and client configuration files.
3 System Evaluation
Considering there are 12 mini PCs, it goes without saying that it is important to ensure the whole system is easy to use. So the basic evaluation of this system is if the system runs stable and if the system is easy to use. On the other hand this system should be able to collect data from multi-sensors in high frequency and high quality. The scalability may be also a way to evaluation this system. The following are some results of this system.
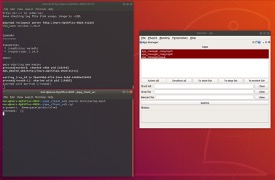
3.1 Manage apps
Open rqt on the master node, you can see the apps of the slave node, you can manage apps by it. As shown below.
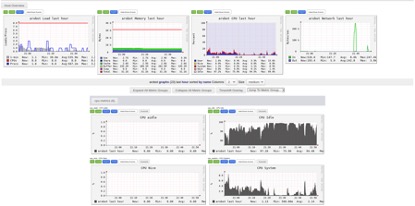
3.2 Monitoring
The graphical interface result of the monitoring tool Ganglin is shown below.
4 Conclusions
This project is a basical system work. We need to focus on tuning the setup of the system instead of re-inventing the wheels. The system can help the data collection of some work which need huge data collection from multisensors like mapping robot. Moreover it can be expanded to many other area like multi-robots and HPRC. Doing this project will give us basic knowledge of construct a distributed system.
Though the main requirements of the system have been realized, there are still some room for improvement. Such as: find a good way to easily copy all collected sensor data from all the PCs (maybe easy with rsync); improve the app manager: change the way of the query mechanism in order to reduce naming conflict; when the slave node is turned on and off, and when the app_manager of the slave node is turned on, provide some appropriate feedback information to the master node; improve the safety performance of the system.
5 Video